
25/06/ · Account of the monetary policy meeting of the Governing Council of the European Central Bank held in Frankfurt am Main on Wednesday and Thursday, June 1. Review of financial, economic and This raises the question of the possibility of adopting a structural rule for the public sector balance, based on structural fundamentals. Full publication: Fiscal Policy, Public Debt and Monetary Fundamentals for FOREX Trading 51 of the markets in certain cases. In others, the data reinforced existing trends. Inflation Control Mechanism Central banks use monetary policy to control aggregate demand and thereby inflation. Economic theorists postulate that monetary policy is a more effective tool when a central bank wants to slow
(PDF) External Factors for the Monetary Policy Transmission Mechanism | Horatiu Dan - blogger.com
Account of the monetary policy meeting of the Governing Council of the European Central Bank held in Frankfurt am Main on Wednesday and Thursday, June Three key conclusions could be drawn on the basis of recent market developments. A drop in coronavirus COVID infection numbers and further large fiscal stimulus measures in other advanced monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals had added to the improved sentiment. Second, the broad-based decline in risk premia on the back of these developments had offset the tightening impact of a deterioration in macroeconomic fundamentals.
While developments in euro area financial markets had, until recently, been broadly consistent with the prospect of a swift economic recovery, expectations were gradually being revised downwards. Third, and as a consequence, the latest easing of financial conditions in the euro area in part hinged on the contribution of fiscal and monetary policy to mitigating fragmentation risks across markets and jurisdictions.
It showed that systemic stress across a range of financial markets had continued to steadily recede, although it remained at an elevated level compared with the period before the coronavirus pandemic in both the euro area and the United States. Global volatility too had abated across various market segments, in part owing to the effective liquidity backstop provided by central banks worldwide. In this environment, overall funding conditions in euro area sovereign bond markets had eased further, as reflected in a downward shift of the euro area GDP-weighted sovereign yield curve, which remained, however, above its pre-crisis level.
Empirical evidence suggested that monetary policy had contributed significantly to the fall in bond yields since the announcement of the pandemic emergency purchase programme PEPP. The PEPP was offsetting upward pressure on bond yields that resulted from the crisis-induced increase in the free float ratio, i.
the share of bonds held by price-sensitive investors relative to total bond supply. Prevailing market segmentation implied that monetary policy needed to act in a more targeted and flexible way to preserve policy transmission across the entire euro area, monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals.
As a result, fiscal and monetary policy in the euro area were starting to act as complements, thereby effectively containing tail risks. Downward pressure on sovereign bond yields had also contributed to monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals funding conditions in euro area corporate bond markets, although they too remained relatively tight compared with the pre-pandemic period.
The exceptionally high pace of gross issuance in the investment grade corporate bond market had not decelerated, highlighting the continued high financing needs of companies, even as lockdown measures were gradually being eased. Financial investment grade commercial paper rates had come down notably in recent weeks from their peaks, while non-financial commercial paper rates had stabilised. Improvements on the debt funding side monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals firms had been accompanied by improvements in equity markets.
The decline since the beginning of was still highest in the euro area, but the Euro Stoxx index had more recently been outperforming other markets following the Franco-German recovery monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals proposal. This easing had, however, been partially offset by deteriorating medium to long-term earnings growth expectations, consistent with a shift in expectations towards a more protracted impact of the crisis.
Mr Lane reviewed the global environment and recent economic and monetary developments in the euro area. The external environment was characterised by a sharp downturn in global activity and trade, which implied a reduction in foreign demand for the euro area. Incoming data confirmed that the global economy had fallen into an unprecedented recession in the first half of the year. The downturn in global trade was expected to be even more severe than the contraction in output as a result of closed borders and disruptions to logistics.
Moreover, trade developments tended to be procyclical, especially in downturns. Data on new export orders pointed to a sharp fall of global trade in the second quarter of the year. Financial conditions had continued to ease in advanced and emerging market economies since the April monetary policy meeting, but remained substantially tighter than before the pandemic shock.
The euro had appreciated somewhat against the US dollar even if it remained broadly unchanged in nominal effective terms. In the euro area, the pandemic and the associated containment measures were taking a toll on productive capacity and domestic demand. In the first quarter of monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals, euro area real GDP had decreased by 3. At a sectoral level, both the manufacturing and services sectors had been severely hit by the pandemic. This had been reflected by PMI business expectations in the manufacturing and services sectors reaching record lows in March and April, before bouncing back somewhat in May.
The pandemic shock had also led to a sharp increase in household savings, as consumption had decreased more strongly than income. The exceptional degree of uncertainty had led to the postponement of consumption and investment with strongly negative effects on growth.
Labour market conditions were rapidly deteriorating and a sizeable decline in euro area trade was expected for the second quarter of Overall, the incoming data pointed to a further significant contraction of real GDP in the second quarter. While euro area activity was expected to rebound in the third quarter as the containment measures were eased further, the overall speed and scale of the rebound remained highly uncertain.
This assessment was broadly reflected in the June Eurosystem staff macroeconomic projections for the euro area. The June projections signalled that output would decline steeply by This was expected to be only partly reversed in the second half of the year, monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals, with quarterly growth rates of 8. Under this baseline, annual output was projected to shrink by 8.
Compared with the March ECB staff macroeconomic projections, the outlook for real GDP growth had been revised substantially downwards by 9. In general, the extent of the contraction and the recovery was seen to depend crucially on the duration and the effectiveness of the containment measures, the success of policies to mitigate the adverse impact on incomes and employment, and the extent to which supply capacity and domestic demand would be permanently affected.
The euro area fiscal stance provided a strong contribution to stabilising GDP growth, based on a combination of discretionary policy measures and the working of automatic stabilisers. However, this was resulting in large increases in deficit and debt. Forthe anticipated strong increase in the euro area government debt-to-GDP ratio was expected to be pushed higher by an unfavourable interest-growth differential. Turning to price developments, headline inflation had dropped further from 0.
The HICP excluding energy and food had remained at 0. Overall measures of underlying inflation had fallen somewhat since February, partly reversing the earlier gradual increases. Pipeline price pressures had weakened and wage negotiations remained monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals hold. On the basis of current and futures prices for oil, headline inflation was likely to decline somewhat further over the coming months and to remain subdued until the end of the year.
Over the medium term, weaker demand was expected to put downward pressure on inflation, which was expected to be only partially offset by upward pressures related to supply constraints. For the long term, survey-based measures of inflation expectations had mostly remained at historical lows, but stood considerably higher than market-based measures.
This assessment was also reflected in the June Eurosystem staff projections, which entailed a substantial downward revision of the inflation outlook in the baseline scenario, with headline inflation expected to average 0. The revisions to the outlook for core inflation indicated an even larger deterioration, with core inflation projected to reach only 0. Compared with the March ECB staff macroeconomic projections, the outlook for HICP inflation had been revised downwards by 0.
While to some extent related to the lower path of energy prices, the revisions also reflected lower price pressures on account of the sharp decline in real GDP and the associated significant increase in economic slack.
The latest EONIA forward curve had also remained largely unchanged, indicating no expectations of a rate cut in Sovereign bond market fragmentation had declined but spreads remained elevated.
A partial recovery in risk asset prices was attributable to an improvement in risk sentiment. Meanwhile, corporate fundamentals continued to deteriorate. Turning to money and credit developments, monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals, broad money M3 growth had increased to 8.
Strong money growth reflected bank credit creation, which was driven to a large extent by the acute liquidity needs in the economy. Moreover, high economic uncertainty was triggering a shift towards money holdings for precautionary reasons.
In this environment, the narrow monetary aggregate M1, encompassing the most liquid forms of money, continued to be the main contributor to broad money growth. The annual growth rate of loans to non-financial corporations rose further to 6. At the same time, the annual growth rate of loans to households decreased to 3. Summing up, Mr Lane observed that the incoming information confirmed that the euro area economy was experiencing an unprecedented contraction.
Survey data and real-time indicators for economic activity had shown some positive signs as the containment measures were gradually eased. Nonetheless, these readings indicated only a minor improvement compared with the speed at which the indicators had plummeted in the preceding two months. The steep decline of output in the second quarter that followed the decline in the first quarter was projected to be only partly reversed in the second half of the year.
Under the baseline, which had been revised substantially downwards relative to the March projections, annual output was projected to shrink by 8. The baseline was surrounded by an exceptional degree of uncertainty. The Monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals staff projections also entailed a substantial downward revision of the inflation outlook in the baseline scenario, with headline inflation expected to average 0.
It was important to note that without the vigorous policy response including an estimated 2. Both the highly accommodative pricing of the targeted longer-term refinancing operations TLTRO III and the collateral easing measures were providing strong incentives for banks to maintain credit flows to the real economy. In addition, the unconditional refinancing operations together with the establishment of international swap lines were ensuring that liquidity in the banking system was protected.
These measures had acted as a stabilising force during this exceptional period. Nevertheless, financial conditions had tightened sharply since the escalation of the pandemic, as the downward shift in risk-free rates had not been fully transmitted to the broader set of asset prices and yields that set the financial conditions monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals the real economy.
In particular, the upward pressure on average sovereign yields had contributed to higher corporate and bank bond yields and a decline in equity valuations, especially for bank stocks. Against this background, Mr Lane emphasised that two main factors called for further policy action at the current meeting.
First, the medium-term outlook for price stability was threatened by the fallout from the coronavirus crisis: in particular, the baseline in the new projections saw 0. Second, financial conditions for the euro area as a whole were significantly tighter compared with the period before the pandemic, whereas the growth and inflation outlook called for easier financial conditions.
In order to counter these pandemic-related negative revisions to the inflation outlook, the appropriate policy response was to increase the size of the PEPP envelope. Against this background, the PEPP was a measure which was proportionate to counter the serious risks to price stability, the monetary policy transmission mechanism and the economic outlook in the euro area, monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals, which are posed by the outbreak and escalating diffusion of COVID Monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals, the downward revision to the inflation outlook, together with the further downside risks captured in the severe scenario, called for a temporary phase of additional asset purchases, in order to deliver the monetary conditions that could support a return to the pre-crisis inflation trajectory within the projection horizon.
In terms of timing, the monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals in the transmission of monetary policy to inflation dynamics meant that it was important to take a significant step in addressing the increase in the inflation shortfall.
Furthermore, the value of a timely response was compounded by the importance of avoiding a sustained unanchoring of inflation expectations, in view of the downside risks faced and the near-term prospect of a sustained phase of very low inflation outcomes.
In terms of the overall monetary stance, the PEPP provided a temporary additional source of accommodation, which operated alongside the more standard suite of policy instruments the level of the ECB policy rates; the APP; forward guidance; and the TLTRO III programme. Given the scale and unique nature of the shock, it was better to tackle the substantial downward shift in the inflation outlook through a targeted and temporary programme the PEPPrather than a recalibration of the existing policy package.
Moreover, an increase in the size of the PEPP envelope would also provide additional protection against the risks of fragmentation across market segments, monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals, which could potentially obstruct the smooth transmission of monetary policy. At the same time, the envelope should be understood as a ceiling, which implied that in the event of significant upside surprises to the outlook, monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals, the full envelope would not need to be used.
Looking ahead, incoming economic and financial data and subsequent projection rounds would provide essential guidance as to whether the pandemic-related negative shock to inflation dynamics had been sufficiently contained. In terms of the overall monetary policy strategy, purchases of government bonds under the PEPP and the APP were an effective tool for delivering on the Treaty-assigned price stability objective in the current environment.
These measures were also efficient, especially in combination with other policy measures, since other instruments would require extraordinary adjustment to generate the same impact on inflation dynamics. The easing of credit conditions would help viable businesses continue to operate and retain as many workers as possible, monetary policy mechanism for forex fundamentals. In turn, preserving jobs was the most important factor in determining incomes and the financial security of individuals and families in the euro area.
Accordingly, the PEPP and the APP were proportionate measures under the current conditions for pursuing the price stability objective, with sufficient safeguards having been built into the design of these programmes to limit potential adverse side effects, including risks of fiscal dominance, and to address the monetary financing prohibition.
On the basis of this assessment,Mr Lane proposed that the Governing Council take the following decisions:.
Trading Boe monetary policy
, time: 1:21Forex Fundamental Analysis
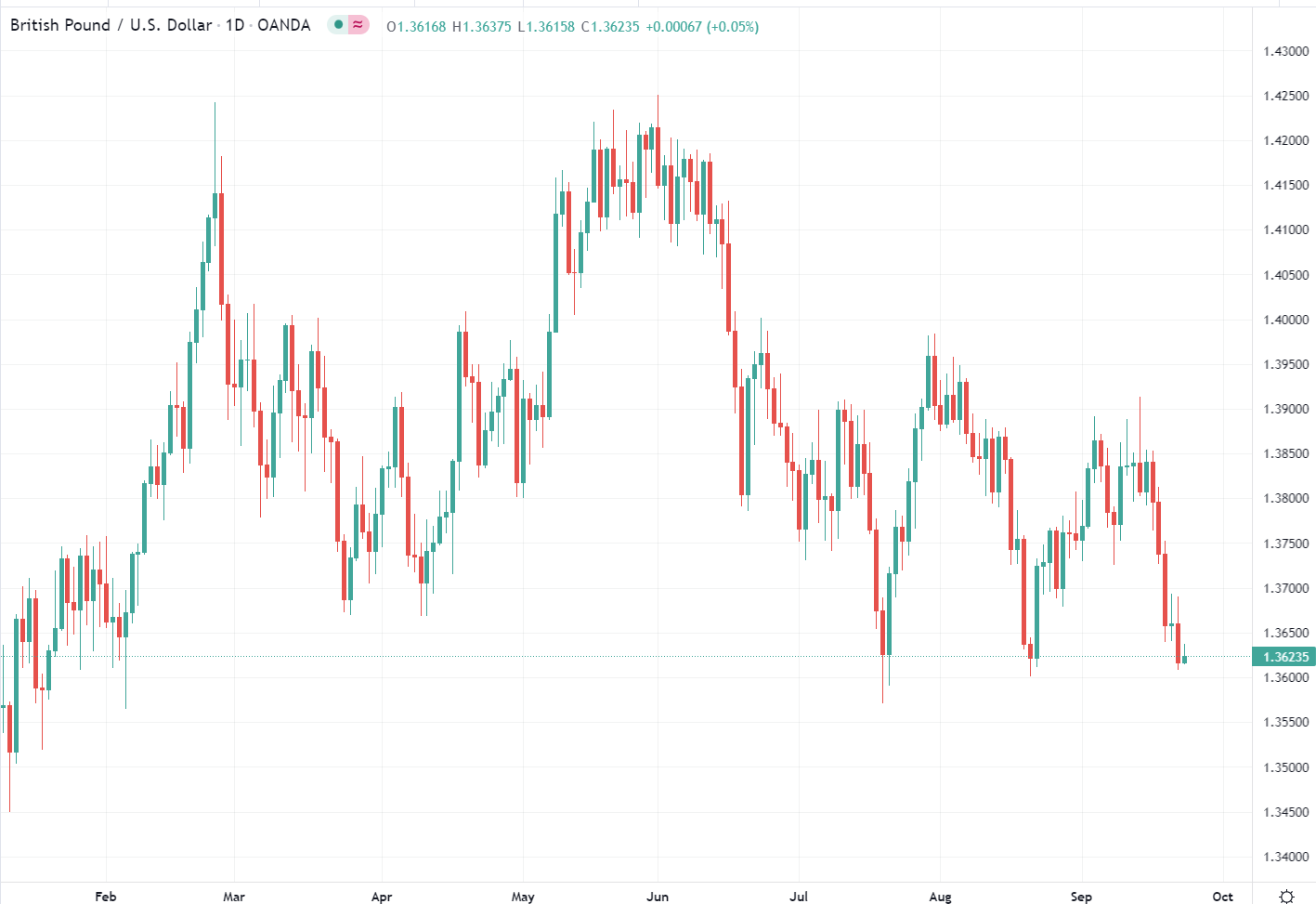
Hawkish vs Dovish: How Monetary Policy Affects FX Trading. Hawkish and dovish policies affect FX rates through a mechanism referred to as 'forward guidance'. Foundational Trading Knowledge. 1 Trade policy, armed conflict and leadership upheavals all create uncertainty in the capital markets. Accounting for these issues as they arise is a vital part of forex fundamental analysis. Understanding how economics, monetary policy and politics can impact investor confidence are the pillars of forex fundamental analysis Monetary policy can be referred to in a couple of different ways. Contractionary or restrictive monetary policy takes place if it reduces the size of the money supply. It can also occur with the raising of interest rates. The idea here is to slow economic growth with high interest rates. Borrowing money becomes harder and more expensive, which
No comments:
Post a Comment